NIH scientists identify nutrient that helps prevent bacterial infection
Media Advisory Friday, January 15, 2021
NIH scientists identify nutrient that helps prevent bacterial infection
Taurine, which helps the body digest fats and oils, could offer treatment benefit.
What
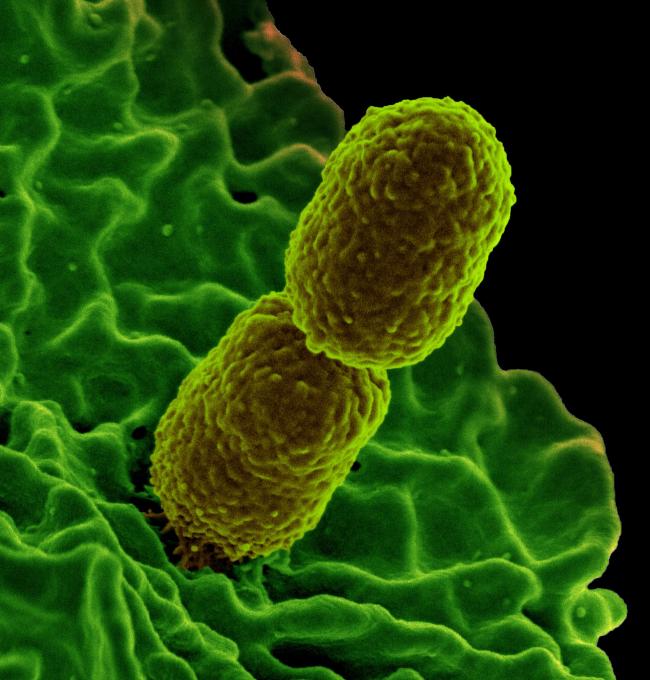
Scientists studying the body’s natural defenses against bacterial infection have identified a nutrient — taurine — that helps the gut recall prior infections and kill invading bacteria, such as Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kpn). The finding, published in the journal Cell by scientists from five institutes of the National Institutes of Health, could aid efforts seeking alternatives to antibiotics.
Scientists know that microbiota — the trillions of beneficial microbes living harmoniously inside our gut — can protect people from bacterial infections, but little is known about how they provide protection. Scientists are studying the microbiota with an eye to finding or enhancing natural treatments to replace antibiotics, which harm microbiota and become less effective as bacteria develop drug resistance.
The scientists observed that microbiota that had experienced prior infection and transferred to germ-free mice helped prevent infection with Kpn. They identified a class of bacteria — Deltaproteobacteria — involved in fighting these infections, and further analysis led them to identify taurine as the trigger for Deltaproteobacteria activity.
Taurine helps the body digest fats and oils and is found naturally in bile acids in the gut. The poisonous gas hydrogen sulfide is a byproduct of taurine. The scientists believe that low levels of taurine allow pathogens to colonize the gut, but high levels produce enough hydrogen sulfide to prevent colonization. During the study, the researchers realized that a single mild infection is sufficient to prepare the microbiota to resist subsequent infection, and that the liver and gallbladder — which synthesize and store bile acids containing taurine — can develop long-term infection protection.
The study found that taurine given to mice as a supplement in drinking water also prepared the microbiota to prevent infection. However, when mice drank water containing bismuth subsalicylate — a common over-the-counter drug used to treat diarrhea and upset stomach — infection protection waned because bismuth inhibits hydrogen sulfide production.
Scientists from NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases led the project in collaboration with researchers from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences; the National Cancer Institute; the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; and the National Human Genome Research Institute.
Article
A Stacy et al. Infection trains the host for microbiota-enhanced resistance to pathogens. Cell DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.011 (2021).
Who
Yasmine Belkaid, Ph.D., chief of NIAID’s Metaorganism Immunity Section in the Laboratory of Immune System Biology, is available to comment.
This news release describes a basic research finding. Basic research increases our understanding of human behavior and biology, which is foundational to advancing new and better ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat disease. Science is an unpredictable and incremental process — each research advance builds on past discoveries, often in unexpected ways. Most clinical advances would not be possible without the knowledge of fundamental basic research. To learn more about basic research at NIH, visit https://www.nih.gov/news-events/basic-research-digital-media-kit.
NIAID conducts and supports research — at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide — to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
Institute/Center
Contact
301-402-1663