AI tool may speed screening of epilepsy drugs in mice
Media Advisory Friday, February 24, 2023
AI tool may speed screening of epilepsy drugs in mice
Machine learning approach automates behavior analysis, outperforms human assessment in animal models of epilepsy.
What
By using state-of-the-art technology to analyze patterns of behavior in mice with epilepsy, researchers may be able to better study the disorder and identify potential treatments. Researchers funded by the National Institutes of Health used the AI technology to determine behavioral “fingerprints” in mice not evident by human eye. Such automated behavioral phenotyping needed only one hour of video recording and did not require researchers to wait for the rare event of a seizure. The study, supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), part of NIH, is published in Neuron.
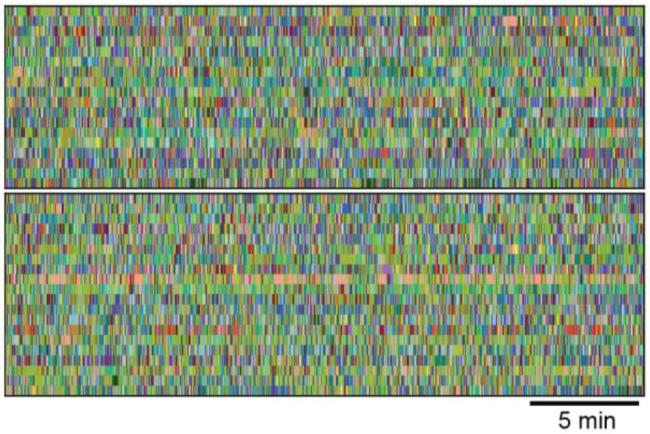
Scientists found that this machine learning-assisted 3D video analysis outperformed the traditional approach, in which analyses rely on human observation to label the behavioral signs of epilepsy in animal models during seizures. The labor-intensive process requires constant video monitoring of the mice over many days or weeks while recording their brain wave activity with electroencephalography (EEG). The team led by Stanford researchers studied mice with acquired and genetic epilepsies. They found that machine analysis was better able to distinguish epileptic vs non-epileptic mice than trained human observers. The AI program also identified distinct behavioral phenotypes at different points in the development of epilepsy.
Notably, researchers were able to use the AI program to distinguish different patterns of behavior in mice after they were given one of three anti-epileptic drugs. This demonstrates that the tool could be used for rapid, automated anti-epileptic drug testing. Ultimately, the use of automated phenotyping for animal studies of the epilepsies could revolutionize how research is done, speeding discovery and reducing costs.
The machine-learning technology used in the study, called MoSeq for Motion Sequencing, locates, tracks, and quantifies the behavior of freely moving mice in each frame of the video. The information is used to train the unsupervised machine learning model to identify repeated motifs of behavior (called “syllables” – e.g., a right turn or headbob to the left). MoSeq predicts the order (or “grammar”) in which syllables occur, allowing fast and objective characterization of mouse behavior.
Who
Vicky Whittemore, Ph.D., program director, NINDS Division of Neuroscience. To arrange an interview, please contact NINDSPressTeam@ninds.nih.gov.
Article
Gschwind et al., Hidden Behavioral Fingerprints in Epilepsy. Neuron. Feb 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2023.02.003
NINDS is the nation’s leading funder of research on the brain and nervous system. The mission of NINDS is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
Institute/Center
Contact
301-496-5751