You are here
News Release
Wednesday, June 12, 2019
NIH-developed technique prevents obstruction in heart valve replacement
BASILICA procedure shows successful results for some high-risk patients.
A novel technique has proven successful in preventing coronary artery obstruction during transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), a rare but often fatal complication. Called Bioprosthetic Aortic Scallop Intentional Laceration to prevent Iatrogenic Coronary Artery obstruction (BASILICA), the technique will increase treatment options for high-risk patients who need heart valve procedures. The findings by researchers at the National Institutes of Health will be published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology: Cardiovascular Interventions on June 12.
TAVR, a procedure used to treat aortic valve stenosis, involves threading a long, thin, flexible tube, called a catheter, through the femoral artery in the leg to the heart. Aortic valve stenosis is a narrowing of the valve controlling blood leaving the heart to the rest of the body. This narrowing reduces blood flow to vital organs, resulting in shortness of breath, chest pain, blackouts, and heart failure.
For elderly or frail patients, TAVR offers an effective and less invasive alternative to open heart surgery. However, a small subset of these patients may develop coronary artery obstruction during the TAVR procedure. For more than half of these patients, this complication has been fatal.
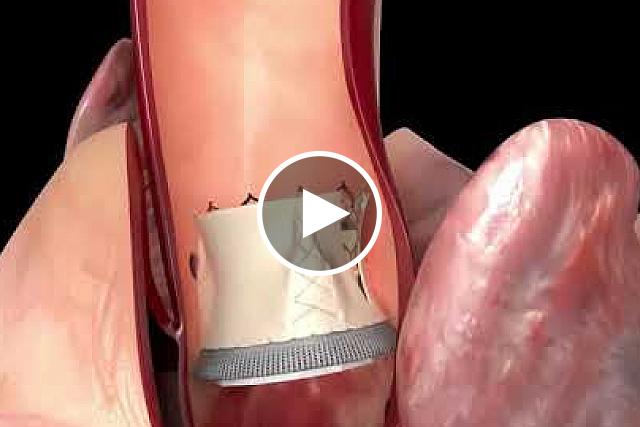
During TAVR, the surgeon places a catheter inside the heart and uses a balloon to open a new valve inside the aortic valve. However, in some patients whose hearts have uncommon structures, such as unusually large valve leaflets or small aortic roots, the large leaflets block the flow of blood to the coronary arteries as the new valve’s scaffolding opens.
BASILICA was developed at the National, Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), part of NIH, to offer a solution to the problem of coronary obstruction during TAVR and increase the safety of TAVR for this subset of patients. The interventional cardiologist weaves an electrified wire the size of a sewing thread through a catheter and uses it to split the original leaflet in two so that it cannot block the coronary artery once it has been pushed aside by the transcatheter heart valve.
After animal experiments proved promising, the researchers successfully performed the procedure on seven patients who qualified for compassionate use of the technique — then untested in humans — because no other care options were available.
The current research builds on the success of the first-in-human trial. From February to July 2018, the BASILICA technique was evaluated in a multicenter early feasibility study, sponsored by NHLBI. It enrolled 30 gravely ill patients who were at high or extreme risk if undergoing surgery.
According to the researchers, all patients survived the procedure and underwent a successful TAVR. BASILICA was successful in 93% of patients and was feasible in natural as well as prosthetic aortic valves. At the 30 days mark, there were no coronary artery obstructions, nor a need to repeat the procedure due to valve dysfunction.
Every year, approximately 5 million people in the United States are diagnosed with heart valve disease, and more than 20,000 die, according to the American Heart Association.
Who
- Robert J. Lederman, M.D., Senior Investigator, NIH, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s (NHLBI) Division of Intramural Research
- Jaffar M. Khan, M.D., staff clinician, NIH, NHLBI
Note: Other researchers contributed substantially to this project, among them, Adam B. Greenbaum, M.D., and Vasilis C. Babaliaros, M.D., from Structural Heart and Valve Center, Emory University Hospital; and Toby Rogers, BM BCh, Ph.D., from Medstar Washington Hospital Center.
Study
J. M. Khan et al. The BASILICA Trial: Prospective Multi-center Investigation of Intentional Leaflet Laceration to Prevent TAVR Coronary Obstruction. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.03.035 June 12, 2019.
About the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): NHLBI is the global leader in conducting and supporting research in heart, lung, and blood diseases and sleep disorders that advances scientific knowledge, improves public health, and saves lives. For more information, visit https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®