You are here
News Release
Wednesday, May 26, 2021
Scientists discover brain cells that compete to sustain or suppress traumatic memories
Two clusters of brain cells compete to promote either the persistence or disappearance of traumatic memories, according to a new study conducted in mice. The findings could provide important insights into human conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and associated problems such as alcohol use disorder (AUD) that can arise from the persistence of traumatic memories. The new research, led by scientists at the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), part of the National Institutes of Health, and their colleagues in Switzerland, is reported in the journal Nature.
“Over time, the distress of having experienced trauma will subside for some people, as memories of the trauma cease to provoke a fearful response,” says NIAAA Director Dr. George F. Koob. “For other people who have experienced trauma, however, the fearful memories persist, and can adversely affect their ability to engage in everyday activities. These fearful memories can continue even though a person may repeatedly encounter cues associated with a traumatic experience without a harm. The current study sheds light on the specific neural circuits that may underlie the persistence and the extinction of fearful memories associated with trauma.”
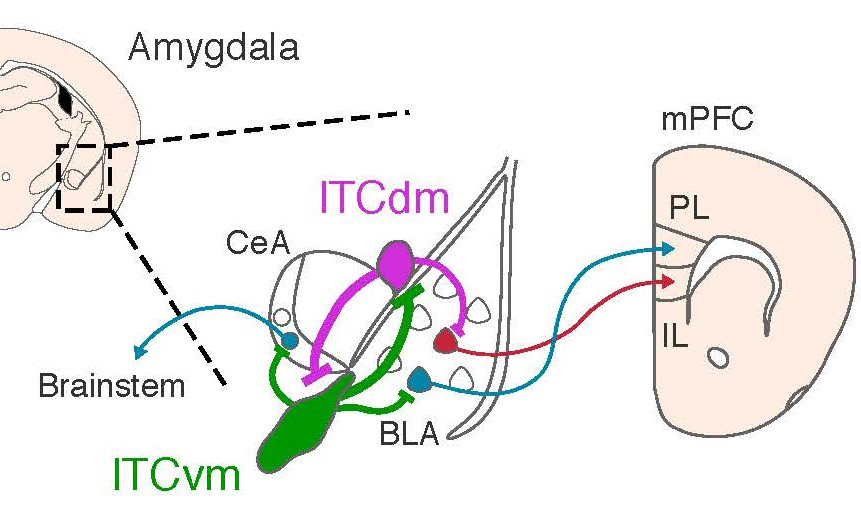
Scientists led by Andrew Holmes, Ph.D., chief of NIAAA’s Laboratory of Behavioral and Genomic Neuroscience, examined clusters of neurons, known as intercalated cells or ITCs, that are packed tightly around the mouse amygdala. Found deep within the temporal lobes of mammals’ brains, the amygdala is well-known as a hub for processing emotions. It is therefore a likely actor in the brain systems that underlie the formation of fearful memories associated with certain environmental cues and the successful extinction of those memories when the same cues later predict no harm.
In a series of behavioral in vivo brain imaging and neurophysiology studies, NIAAA scientists collaborated with researchers in the United States, Switzerland and Germany to assess the potential roles of ITCs as mice learned to associate a cue (e.g., a sound) with a foot-shock (a fear-inducing event), and then extinguished the association by no longer pairing the cue with a foot-shock.
The researchers found that two distinct ITC clusters promote either a fear response or extinction of the cue / foot-shock association. They further revealed that the clusters effectively compete with one another, through a process known as mutual synaptic inhibition, to determine the relative strength of each memory and, hence, the level of defensive behavior shown by the animal. The study also showed that the ITC clusters have long-range connections to known fear-regulating regions in the midbrain and prefrontal cortex.
“The persistence of disturbing memories of a traumatic event are one of the hallmarks of PTSD and some anxiety disorders,” says Dr. Holmes. “Our findings identify a neural circuit within the amygdala that orchestrates activity across a broad brain network to exert a powerful influence over the ability to switch between high and low fear states. This finding now raises interesting questions about whether dysfunction of this brain system could contribute to the marked individual differences in risk for trauma-related psychiatric disorders.”
This news release describes a basic research finding. Basic research increases our understanding of human behavior and biology, which is foundational to advancing new and better ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat disease. Science is an unpredictable and incremental process — each research advance builds on past discoveries, often in unexpected ways. Most clinical advances would not be possible without the knowledge of fundamental basic research. To learn more about basic research at NIH, visit https://www.nih.gov/news-events/basic-research-digital-media-kit.
About the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA): The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), part of the National Institutes of Health, is the primary U.S. agency for conducting and supporting research on the causes, consequences, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of alcohol use disorder. NIAAA also disseminates research findings to general, professional, and academic audiences. Additional alcohol research information and publications are available at https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
Reference
KM Hagihara, O Bukalo, M Zeller, A Aksoy-Aksel, N Karalis, A Limoges, T Rigg, T Campbell, A Mendez, C Weinholtz, M Mahn, LS Zweifel, RD Palmiter, I Ehrlich, A Lüthi & A Holmes. Intercalated amygdala clusters orchestrate a switch in fear state. Nature. Published online May 26, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03593-1