You are here
Media Advisory
Wednesday, May 14, 2025
NIH researchers discover tissue biomarker that may indicate higher risk of aggressive breast cancer development and death
What
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have identified a series of changes in the architecture and cell composition of connective tissues of the breast, known as stromal tissue, that is associated with an increased risk of developing aggressive breast cancer among women with benign breast disease, and poorer rates of survival among women with invasive breast cancer. This process, which they call stromal disruption, could potentially be used as a biomarker to identify women with benign breast disease who are at high risk of developing aggressive breast cancers, as well as those with breast cancer who may be at increased risk of recurrence or death.
Such insights could help inform the development of cancer prevention and treatment strategies that target the stromal microenvironment. In addition, stromal disruption is inexpensive to assess and could be widely adopted, particularly in low-resource settings where molecular analysis is impractical or very expensive.
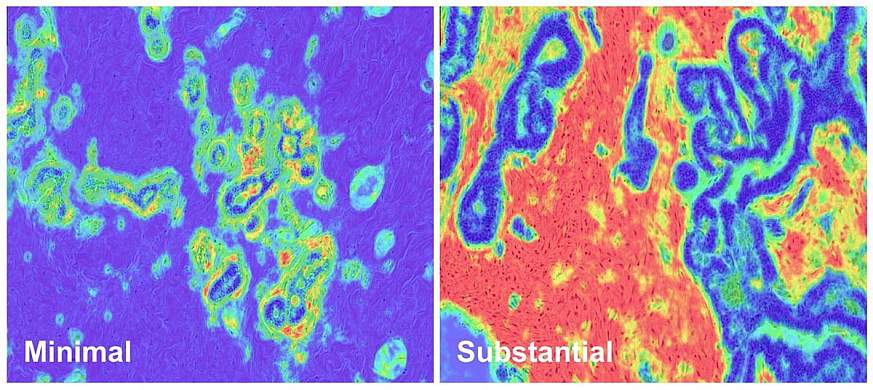
In the study, the researchers used machine learning to detect subtle changes in the stroma of 4,023 donated samples of healthy breast tissue, 974 biopsies of tissue with benign breast disease, and 4,223 biopsies of tissue with invasive breast cancer.
- In women who donated healthy breast tissue, the same risk factors associated with aggressive breast cancer— including younger age, having two or more children, being self-reported as Black, obesity, and family history—were also associated with increased stromal disruption, suggesting that those risk factors may act via a common stromal tissue pathway.
- In women with benign breast disease, having substantial stromal disruption on biopsy was associated with a higher risk of developing aggressive breast cancer and more rapid onset of breast cancer than having minimal or no stromal disruption.
- In women with invasive breast cancer, increased stromal disruption was associated with more aggressive disease phenotypes and poorer survival outcomes, particularly for women with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer, the most common subtype.
The researchers noted that factors such as chronic inflammation and wound healing play a role in stromal disruption. They emphasized the need for additional studies to determine whether strategies to prevent these tissue changes from occurring, such as lifestyle changes and anti-inflammatory medications, might be beneficial to reduce aggressive breast cancer risk, particularly among high-risk women.
Who
Mustapha Abubakar, M.D., Ph.D., Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute
Reference
“Unraveling the role of stromal disruption in aggressive breast cancer etiology and outcomes” appears May 14, 2025, in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
About the National Cancer Institute (NCI): NCI leads the National Cancer Program and NIH’s efforts to dramatically reduce the prevalence of cancer and improve the lives of people with cancer. NCI supports a wide range of cancer research and training extramurally through grants and contracts. NCI’s intramural research program conducts innovative, transdisciplinary basic, translational, clinical, and epidemiological research on the causes of cancer, avenues for prevention, risk prediction, early detection, and treatment, including research at the NIH Clinical Center—the world’s largest research hospital. Learn more about the intramural research done in NCI’s Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics. For more information about cancer, please visit the NCI website at cancer.gov or call NCI’s contact center at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
